

Only somatic cells (any cell besides sex cells, sperm and egg) reproduce by mitosis.
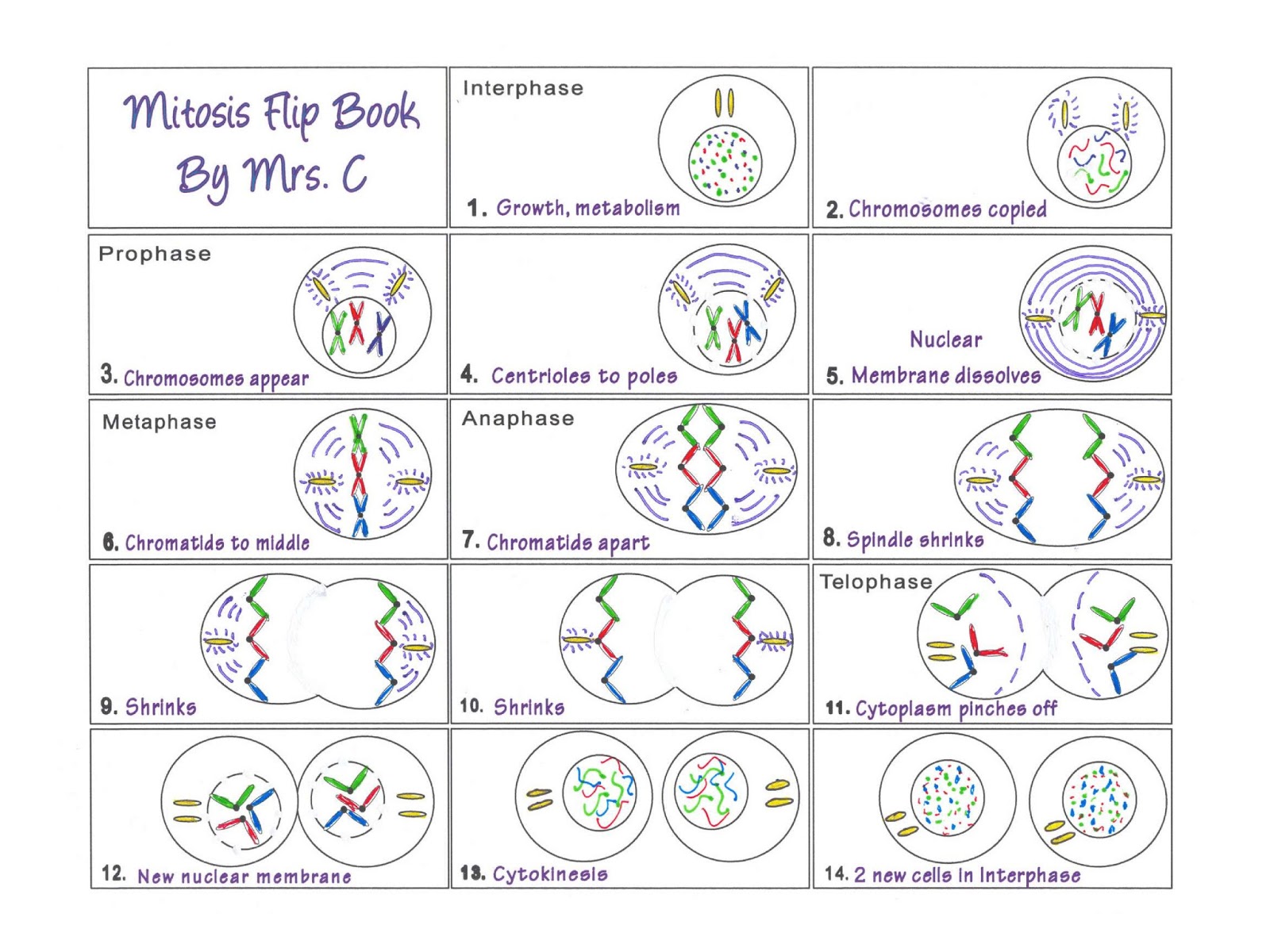
The daughter cells are identical to one another and to the original parent cell. Tyson JJ, Novak B (2008) Temporal organization of the cell cycle. Introduction: Mitosis is a process of cell division which results in the production of two daughter cells from a single parent cell. Interphase is the longest part of the cell cycle. Schwob E, Bohm T, Mendenhall MD, Nasmyth K (1994) The B-type cyclin kinase inhibitor p40SIC1 controls the G1 to S transition in S. In eukaryotic cells, the cell cycle is divided into two major phases: interphase and mitosis (or the mitotic (M) phase). Potapova TA, Daum JR, Pittman BD, Hudson JR, Jones TN, Satinover DL, Stukenberg PT, Gorbsky GJ (2006) The reversibility of mitotic exit in vertebrate cells. End on the 12th page with a drawing of cytokinesis, where the cell is split into two cells. Novak B, Tyson JJ, Gyorffy B, Csikasz-Nagy A (2007) Irreversible cell-cycle transitions are due to systems-level feedback. Again, continue on the 10th and 11th pages with middle and late Telophase. Murray AW (1992) Creative blocks: cell-cycle checkpoints and feedback controls.

Morgan DO (2007) The cell cycle: Principles of control. Students will read, label, and color all the phases of cell reproduction- from interphase through cytokinesis. Minshull J, Pines J, Golsteyn R, Standart N, Mackie S, Colman A, Blow J, Ruderman JV, Wu M, Hunt T (1989) The role of cyclin synthesis, modification and destruction in the control of cell division. CrazyScienceLady This resource includes a mitosis flip book: just print and fold. 4.8 (140) PDF Add one to cart Wish List Mitosis: Flip Book and Onion Root Lab Created by CrazyScienceLady This resource includes a mitosis flip book: just print and fold. Michael WM, Newport J (1998) Coupling of mitosis to the completion of S phase through Cdc34-mediated degradation of Wee1.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
